In the realm of skincare concerns, acne reigns supreme as a common and often frustrating issue. Among the various types of acne, comedonal acne stands out for its distinct characteristics and impact on skin health. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of comedonal acne, exploring its symptoms, causes, treatment options, and effective prevention strategies. Whether you’re dealing with comedonal acne or seeking knowledge to help others, this guide aims to provide valuable insights for achieving clear and radiant skin.
What is Comedonal Acne?
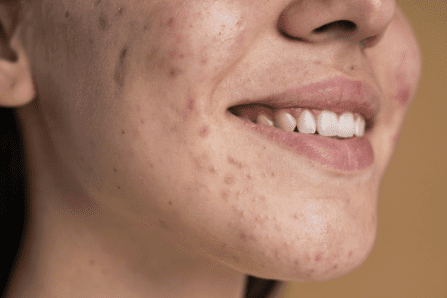
Definition and Characteristics Comedonal acne, often referred to as non-inflammatory acne, is a type of acne characterized by the presence of comedones—small, flesh-colored or dark bumps on the skin. Comedones develop when hair follicles become clogged with a combination of sebum (skin oil) and dead skin cells. While comedones themselves are not typically painful or inflamed, they can be a precursor to other types of acne lesions.
Distinction from Other Types of Acne Comedonal acne is distinct from inflammatory acne, which includes pustules, papules, nodules, and cysts. Unlike inflammatory acne, comedonal acne does not involve redness, swelling, or pus-filled lesions. Understanding this distinction is crucial for tailoring an effective treatment and prevention plan.
Symptoms of Comedonal Acne:
- Closed Comedones (Whiteheads):
Closed comedones, commonly known as whiteheads, appear as small, raised bumps with a white or flesh-colored top. These comedones occur when the clogged hair follicle remains closed at the surface of the skin, preventing exposure to air.
- Open Comedones (Blackheads):
Open comedones, often called blackheads, are similar to closed comedones but have a dark or black appearance. This color results from the oxidation of melanin in the trapped sebum and dead skin cells. Unlike closed comedones, open comedones have an exposed opening at the surface of the skin.
Causes of Comedonal Acne:
- Excess Sebum Production:
One of the primary contributors to comedonal acne is the overproduction of sebum. This excess oil combines with dead skin cells, creating an environment conducive to comedone formation.
- Impaired Skin Cell Turnover:
Healthy skin undergoes a natural process of shedding dead skin cells and replacing them with fresh ones. In individuals with comedonal acne, this process may become disrupted, leading to the accumulation of dead skin cells that contribute to clogged pores.
- Hormonal Fluctuations:
Hormonal changes, particularly during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, can influence sebum production and contribute to the development of comedonal acne.
- Cosmetics and Skincare Products:
Certain cosmetics and skincare products containing comedogenic ingredients can exacerbate comedonal acne by further clogging pores. It’s important to choose non-comedogenic products that do not contribute to pore blockage.
Treatment of Comedonal Acne:
- Topical Retinoids:
Topical retinoids, derived from vitamin A, are highly effective in promoting skin cell turnover and preventing the formation of comedones. They help unclog pores and encourage the shedding of dead skin cells.
- Salicylic Acid:
Salicylic acid is a beta hydroxy acid that exfoliates the skin’s surface and penetrates pores, effectively removing debris and preventing comedone formation.
- Benzoyl Peroxide:
Benzoyl peroxide acts as an antimicrobial agent, targeting the bacteria that contribute to acne. It also helps to reduce excess oil production and clear clogged pores.
- Professional Extraction:
A trained dermatologist or esthetician can perform professional comedone extraction using specialized tools. This process can help remove stubborn comedones safely and effectively.
- Chemical Peels:
Chemical peels involve the application of a solution to the skin, causing exfoliation and the removal of dead skin cells. This process can help improve skin texture, unclog pores, and reduce comedonal acne.
Prevention of Comedonal Acne
- Proper Skincare:
Routine Establishing a consistent skincare routine is crucial for preventing comedonal acne. This routine should include gentle cleansing, exfoliation, and moisturization to maintain balanced and healthy skin.
- Hydration and Diet:
Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and nutrients can contribute to overall skin health and prevent excessive sebum production.
- Avoiding Comedogenic Products:
Choose skincare and cosmetic products labeled as non-comedogenic or oil-free to minimize pore-clogging potential.
- Regular Exfoliation:
Incorporating regular exfoliation into your skincare routine helps remove dead skin cells, preventing their accumulation and reducing the likelihood of comedone formation.
When to Seek Professional Help:
- Persistent or Severe Acne If comedonal acne persists despite diligent skincare efforts, consulting a dermatologist is recommended. They can provide personalized treatment options tailored to your skin’s needs.
- Scarring and Hyperpigmentation If comedonal acne lesions are manipulated or picked at, scarring and hyperpigmentation may occur. A dermatologist can provide guidance on managing and treating these post-acne concerns.
Lifestyle Habits for Healthy Skin:
- Stress Management:
Chronic stress can exacerbate acne by triggering hormonal fluctuations. Engaging in stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can have a positive impact on skin health.
- Adequate Sleep:
Quality sleep is essential for skin repair and regeneration. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night to support overall skin wellness.
- Exercise and Physical Activity:
Regular exercise promotes healthy blood circulation, which can contribute to vibrant and nourished skin. Remember to cleanse your skin after sweating to prevent pore blockage.
Conclusion:
Comedonal acne may not be as visibly inflammatory as other types of acne, but it’s impact on skin health and self-esteem can still be significant. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for comedonal acne, you are better equipped to make informed decisions about your skincare routine. Whether you choose topical treatments, professional interventions, or preventive measures, the journey to achieving clear and radiant skin is within reach. Remember, consistency and patience are key, and seeking professional guidance when needed can make all the difference in your path to healthier, more confident skin.


